PhotoShop算法原理解析系列 - 像素化-碎片
时间:2023/7/9作者:未知来源:手揣网教程人气:
- [摘要]接着上一篇文章的热度,继续讲讲一些稍微简单的算法吧。 本文来讲讲碎片算法,先贴几个效果图吧: 这是个破坏性的滤镜,拿美女来说事是因为搞图像的人90...接着上一篇文章的热度,继续讲讲一些稍微简单的算法吧。
本文来讲讲碎片算法,先贴几个效果图吧:




这是个破坏性的滤镜,拿美女来说事是因为搞图像的人90%是男人,色色的男人。
关于碎片滤镜的原理,网络上可找到的资料为:将图像创建四个相互偏移的副本,产生类似重影的效果。
就凭上述一句话,我们就可以动手了。
分析:通过上述几幅图像的比较,特别是眼睛部位,可以看出处理的图应该看得出像是单眼变成了4个眼睛,因此,网络上的说法可靠。
那么偏移的中心在哪里,偏移的数量又是多少呢,4个偏移,分别是往那些方向偏移呢,这些问题也很简单,可以那PS做验证:
具体步骤如下:打开一幅图像,在图像颜色比较单调的地方(比如上述美女的手臂处)填充一处2*2像素的红色,然后复制图层,对复制后的图层进行碎片滤镜处理,并调整图层透明度为50%,局部放大可得到如下图像:
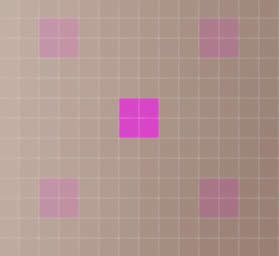
如此效果,则可轻易得出结论:
偏移的中心就是以每个像素为中心,4个偏移分别以中心对称,斜45度均匀圆周布置,水平和垂直偏移各45度,偏移量4个像素。
那么如何叠加的问题应该可以猜测,是取四次偏移后累加值的平均值。
针对如此思路,我写出如下算法:
private void CmdFragment_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { int X, Y, Z, XX, YY; int Width, Height, Stride; int Speed, Index; int SumR, SumG, SumB; Bitmap Bmp = (Bitmap)Pic.Image; if (Bmp.PixelFormat != PixelFormat.Format24bppRgb) throw new Exception("不支持的图像格式."); Width = Bmp.Width; Height = Bmp.Height; Stride = (int)((Bmp.Width * 3 + 3) & 0XFFFFFFFC); byte[] ImageData = new byte[Stride * Height]; // 用于保存图像数据,(处理前后的都为他) byte[] ImageDataC = new byte[Stride * Height]; // 用于保存克隆的图像数据 int[] OffsetX = new int[] { 4, -4, -4, 4 }; // 每个点的偏移量 int[] OffsetY = new int[] { -4, -4, 4, 4 }; fixed (byte* P = &ImageData[0], CP = &ImageDataC[0]) { byte* DataP = P, DataCP = CP; BitmapData BmpData = new BitmapData(); BmpData.Scan0 = (IntPtr)DataP; // 设置为字节数组的的第一个元素在内存中的地址 BmpData.Stride = Stride; Bmp.LockBits(new Rectangle(0, 0, Bmp.Width, Bmp.Height), ImageLockMode.ReadWrite ImageLockMode.UserInputBuffer, PixelFormat.Format24bppRgb, BmpData); Stopwatch Sw = new Stopwatch(); // 只获取计算用时 Sw.Start(); System.Buffer.BlockCopy(ImageData, 0, ImageDataC, 0, Stride * Height); // 填充克隆数据 for (Y = 0; Y < Height; Y++) { Speed = Y * Stride; for (X = 0; X < Width; X++) { SumB = 0; SumG = 0; SumR = 0; for (Z = 0; Z < 4; Z++) // 累积取样点的取样和 { XX = X + OffsetX[Z]; YY = Y + OffsetY[Z]; if (XX < 0) // 注意越界 XX = 0; else if (XX >= Width) XX = Width - 1; if (YY < 0) YY = 0; else if (YY >= Height) YY = Height - 1; Index = YY * Stride + XX * 3; SumB += DataCP[Index]; SumG += DataCP[Index + 1]; SumR += DataCP[Index + 2]; } DataP[Speed] = (byte)((SumB+2) >> 2); // 求平均值(Sum+2)/4,为什么要+2,就为了四舍五入。比如如果计算结果为108.6,则取像素109更为合理 DataP[Speed + 1] = (byte)((SumG + 2) >> 2); DataP[Speed + 2] = (byte)((SumR + 2) >> 2); Speed += 3; // 跳往下一个像素 } } Sw.Stop(); this.Text = "计算用时: " + Sw.ElapsedMilliseconds.ToString() + " ms"; Bmp.UnlockBits(BmpData); // 必须先解锁,否则Invalidate失败 } Pic.Invalidate();}算法中,OffsetX 和 OffsetY分别为取样点像素的偏移量。同样,由于该滤镜涉及到了领域操作,在处理前需要做像素备份,但这里没有对备份数据进行扩展。因此,在内部代码里就需要对取样点的坐标进行验证,看是否超过其范围,如果超过范围,通常在图像滤镜算法范围内,有3种处理方式:
(1)超过了则认为是其最接近的边界值,即重复边缘像素,这部分代码即上述贴出的if ..... else if 部分。
(2)折回,可用如下代码来描述:
while (XX >= Width) XX = XX - Width;while (XX < 0) XX = XX + Width;while (YY >= Height) YY = YY - Height;while (YY < 0) YY = YY + Height;(3) 只计算在图像范围内的像素:
if (XX >= 0 && XX < Width && YY >= 0 && YY < Height) { // 累加计算 }当然这样做,就必须用一个变量记录下都做了多少次符合条件的计算。
有兴趣的朋友可以自己改改代码试一试。
上述代码段中DataP[Speed] = (byte)((SumB+2) >> 2);要对SumB加2的原因是为了让结果进行四舍五入的操作,这样才较为合理。
经过测试,上述代码和PS处理的效果100%的吻合。说明我们的猜测是完全正确的。
还可以对算法进一步扩展: 想的远一点,为什么非的是4个重影呢,非得是45度角度呢,非得是4个像素的水平和垂直偏移呢。我给出下图让有兴趣的读者自己研发吧。
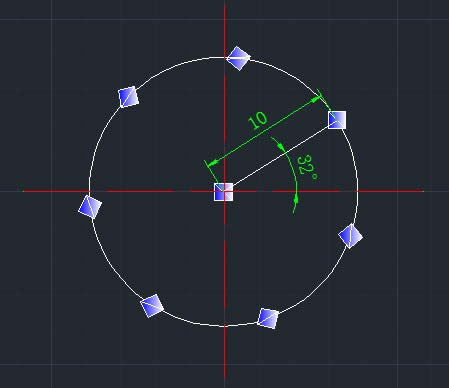
图中,角度为32度,半径为10,碎片数为7,可产生类似下面的效果(可用我的Imageshop进行验证):


更多PhotoShop算法原理解析系列 - 像素化-碎片相关文章请关注PHP中文网!
Photoshop默认保存的文件格式,可以保留所有有图层、色版、通道、蒙版、路径、未栅格化文字以及图层样式等。
关键词:PhotoShop算法原理解析系列 - 像素化-碎片